Social Emotional Learning Curriculum PDF: A Comprehensive Plan
Recent developments showcase districts utilizing federal COVID-19 relief funds for SEL investments, mirroring a growing trend amid ongoing cultural debates and curriculum scrutiny․
What is Social Emotional Learning (SEL)?
Social Emotional Learning (SEL), while gaining prominence now, actually traces its roots back to the 1960s, evolving significantly over the decades․ At its core, SEL focuses on developing a student’s self-awareness, self-management skills, social awareness, relationship skills, and responsible decision-making abilities․
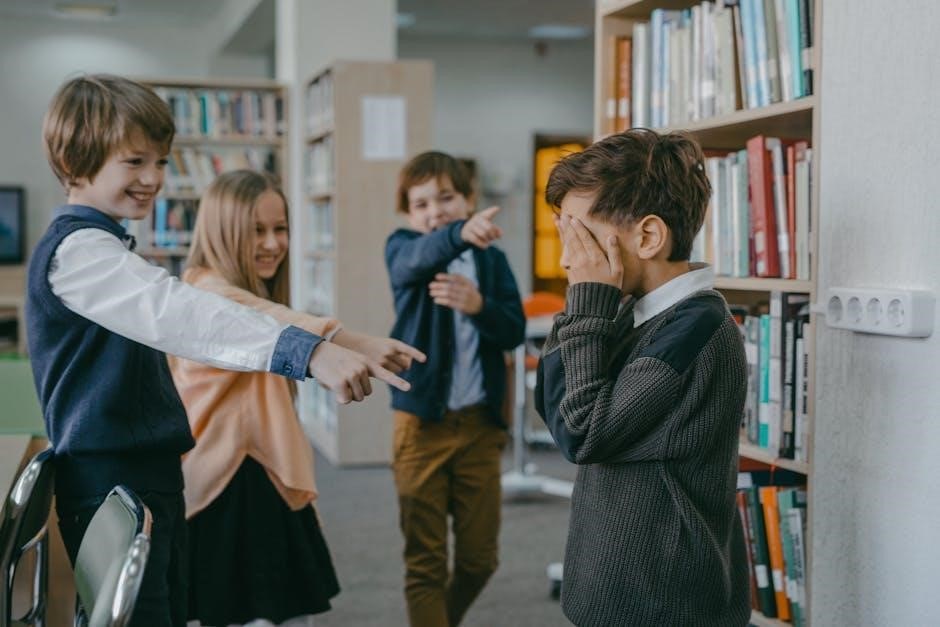
It’s about equipping young people not just with academic knowledge, but also with the crucial life skills needed to navigate emotions, build strong relationships, and make ethical choices․ The recent surge in SEL implementation, often funded by COVID-19 relief, reflects a growing recognition of its importance, particularly in addressing behavioral issues observed in schools – like the return to distance learning at Reynolds Middle School due to such concerns․

However, SEL isn’t without its critics, often becoming entangled in broader cultural and political debates, similar to past controversies surrounding Common Core and Critical Race Theory․
The History and Evolution of SEL
The origins of SEL can be traced back to the 1960s, initially emerging from fields like developmental psychology and education․ Early efforts focused on understanding and fostering children’s emotional development, but lacked the comprehensive framework we see today․ Over time, research highlighted the link between emotional intelligence and academic success, leading to increased interest in integrating SEL into school curricula․
The concept gained further traction with the work of researchers like Daniel Goleman, popularizing the term “emotional intelligence․” More recently, the focus has shifted towards standardized frameworks, like CASEL’s, and evidence-based programs, such as Second Step and RULER․ The current wave of SEL implementation, fueled by federal funding, represents a significant expansion, though it also faces scrutiny and debate, mirroring past educational reforms․
This evolution demonstrates a growing understanding of the holistic needs of students․
Key Components of an Effective SEL Curriculum
A robust SEL curriculum transcends simply teaching emotional vocabulary; it necessitates a systemic approach․ Core components include explicit instruction in self-awareness, self-management, social awareness, relationship skills, and responsible decision-making․ Effective programs integrate these skills across all school settings, not just dedicated lessons․
Crucially, curricula must be evidence-based, demonstrating measurable improvements in student behavior and academic outcomes․ Implementation requires ongoing professional development for teachers, equipping them to model and facilitate SEL practices․ Furthermore, a successful curriculum actively involves families and the wider community, fostering a consistent message about emotional well-being․
Addressing behavioral issues, like those seen at Reynolds Middle School, highlights the practical need for these components․
CASEL Framework: The Core SEL Competencies
The Collaborative for Academic, Social, and Emotional Learning (CASEL) provides a widely recognized framework for SEL, outlining five interconnected core competencies․ These aren’t isolated skills, but rather building blocks for holistic development․ Self-awareness involves recognizing emotions and their impact, while self-management focuses on impulse control and stress management․
Social awareness emphasizes empathy and understanding diverse perspectives․ Relationship skills encompass effective communication and collaboration․ Finally, responsible decision-making promotes ethical considerations and problem-solving․ Programs like Second Step and RULER often align with this framework, providing structured approaches to cultivate these competencies․
The increasing adoption of SEL, despite controversies, underscores the perceived value of CASEL’s guidance in structuring effective curricula․
Self-Awareness and its Importance
Self-awareness, a cornerstone of SEL, involves accurately recognizing one’s own emotions, strengths, weaknesses, and values․ It’s about understanding how these internal factors influence thoughts and behaviors․ This competency isn’t simply introspection; it’s about connecting internal states to external reactions, fostering emotional regulation․
Within a curriculum, activities modeling emotions – like identifying “surprised” – are crucial for young learners․ For older students, this evolves into analyzing personal biases and understanding their impact on interactions․ Developing self-awareness is vital for building empathy, improving relationships, and making responsible decisions․
Without this foundational skill, students may struggle to navigate social situations effectively, hindering their overall well-being and academic success․
Self-Management Strategies
Self-management, building upon self-awareness, equips individuals with the ability to regulate emotions, thoughts, and behaviors effectively․ This isn’t about suppressing feelings, but rather responding to them in a healthy and constructive manner․ Curriculum PDFs often include techniques like deep breathing exercises, mindfulness practices, and stress-reduction strategies․
For middle school students, analyzing lyrics – a “grinding it out” mentality – can be framed as a self-management exercise, promoting resilience․ Addressing behavioral issues, as seen in Reynolds Middle School’s return to distance learning, highlights the need for proactive self-management skills․
Effective strategies empower students to persevere through challenges, set goals, and take initiative, fostering a sense of agency and control over their lives․
Social Awareness: Understanding Others
Social awareness within SEL curricula focuses on developing empathy and perspective-taking skills․ PDFs emphasize recognizing and understanding the emotions, thoughts, and cultural backgrounds of others․ This component moves beyond simply acknowledging differences to actively valuing diverse viewpoints․
The core of SEL, as suggested by the focus on empathy, relies heavily on this understanding․ Programs like Social Perspectives, described as “comprehensive and evidence-based,” likely dedicate significant portions to fostering social awareness․
Cultivating this skill is crucial in navigating complex social situations and building positive relationships․ It’s a direct response to the “culture-war controversy” surrounding education, promoting inclusivity and respectful dialogue․
Relationship Skills: Building Connections
Relationship skills, a vital component detailed in SEL curriculum PDFs, concentrate on establishing and maintaining healthy, fulfilling relationships․ This includes effective communication, active listening, cooperation, and conflict resolution strategies․
These skills are particularly relevant given recent instances of behavioral issues in schools, like Reynolds Middle School’s return to distance learning․ A well-designed SEL curriculum aims to equip students with the tools to navigate social interactions constructively․

Programs emphasize modeling positive behaviors and providing opportunities for practice․ The focus isn’t solely on avoiding conflict, but on learning how to address disagreements respectfully and collaboratively, fostering a positive school climate․
Responsible Decision-Making in SEL
Responsible decision-making, as outlined in SEL curriculum PDFs, empowers students to consider ethical norms and safety concerns when making choices․ It involves accurately assessing risks and benefits, reflecting on consequences, and understanding personal values․
This competency is increasingly crucial amidst ongoing debates surrounding educational approaches, like Common Core and Critical Race Theory, where curriculum choices are heavily scrutinized․ SEL aims to foster thoughtful, informed citizens․
Curricula often incorporate scenarios and role-playing exercises to help students practice these skills․ The goal is to move beyond impulsive reactions and cultivate a proactive approach to problem-solving, promoting positive outcomes for themselves and their communities․
Benefits of Implementing SEL in Schools
Implementing SEL, often supported by readily available curriculum PDFs, yields significant benefits for students and school climates․ Reports indicate reduced behavioral issues, as seen in Reynolds Middle School’s return to in-person learning after addressing disruptions․
SEL fosters improved academic performance by enhancing focus and engagement․ Furthermore, it cultivates a more positive and supportive learning environment, benefiting both students and teachers․ Districts like Omaha Public Schools are investing substantial funding into SEL initiatives․
These programs equip students with essential life skills, promoting emotional regulation, empathy, and responsible decision-making, ultimately preparing them for success beyond the classroom, despite ongoing controversies surrounding educational practices․
SEL Curriculum Examples & Providers
Numerous SEL programs, often accessible as downloadable PDFs, are available for schools․ The Second Step program stands out as a widely utilized resource, offering comprehensive lessons and materials․ Another prominent approach is RULER, developed at Yale, focusing on recognizing, understanding, labeling, expressing, and regulating emotions․
Social Perspectives is highlighted as a comprehensive, evidence-based curriculum․ These programs often include resources for teachers, student workbooks, and family engagement materials, frequently available in PDF format for easy implementation․
Texas State University is partnering with school districts to implement and research SEL curriculum effectiveness․ The variety of providers reflects the growing demand for effective SEL solutions, addressing diverse student needs and school contexts․
Second Step Program Overview
The Second Step program is a widely adopted, research-based SEL curriculum often available in PDF format for educators․ It focuses on skills like empathy, emotion management, and problem-solving, delivered through engaging lessons and activities․ The program is structured for different grade levels, offering age-appropriate content from preschool through middle school․
Key components include lessons on recognizing and responding to emotions in oneself and others, developing friendship skills, and handling challenging situations constructively․ Educators can access comprehensive teaching materials, including lesson plans, student materials, and family letters, often as downloadable PDFs․
Second Step aims to create a positive school climate and improve student outcomes by fostering social-emotional competence․ It’s a frequently cited example when discussing SEL curriculum PDFs․

RULER Approach to SEL
The RULER approach, developed at Yale Center for Emotional Intelligence, is another prominent SEL framework frequently found as a downloadable PDF resource for schools․ RULER stands for Recognizing, Understanding, Labeling, Expressing, and Regulating emotions – a practical guide for building emotional intelligence․
Unlike some curricula focused solely on students, RULER emphasizes equipping educators with the skills to model and teach emotional intelligence․ The program provides professional development for teachers, alongside classroom materials and family resources, often available in PDF format․
RULER aims to create emotionally literate school communities where feelings are openly acknowledged and skillfully managed․ It’s a comprehensive system designed to improve school climate and student well-being, and is a popular choice for SEL curriculum implementation․
Accessing SEL Curriculum PDFs: Free and Paid Resources
Numerous organizations offer Social Emotional Learning (SEL) curriculum materials in PDF format, ranging from free resources to comprehensive, paid programs․ Many school districts are leveraging federal funding, like the $460,000 allocated in Omaha, Nebraska, to invest in these resources․
Free PDFs often include lesson plans, activity sheets, and introductory guides from organizations promoting SEL․ Paid curricula, like Second Step and RULER, typically offer more extensive materials, professional development, and ongoing support․ These often require a purchase or subscription for full access to the PDF content․
Online searches for “SEL curriculum PDF” yield a variety of options, but careful evaluation of the source and alignment with school goals is crucial․ Districts are actively seeking and implementing these curricula to address student behavioral needs and improve school climate․

SEL Implementation Challenges and Solutions

Implementing Social Emotional Learning (SEL) curricula, even with accessible PDF resources, presents challenges․ Reynolds Middle School’s return to distance learning due to behavioral issues highlights a key hurdle: addressing pre-existing student needs before introducing SEL concepts․ Opposition to SEL, mirroring debates around Common Core and Critical Race Theory, also creates resistance․
Solutions involve comprehensive teacher training, ensuring buy-in from staff and the community, and demonstrating the curriculum’s evidence-based effectiveness․ Clear communication about SEL’s goals – fostering empathy and responsible decision-making – can counter misinformation․
Furthermore, consistent implementation across all school levels is vital․ Districts must allocate sufficient resources, not just for the PDF materials, but also for ongoing support and evaluation of program impact․ Addressing root causes of behavioral issues alongside SEL is crucial for success․
The Role of Teachers in SEL Implementation
Teachers are central to successful Social Emotional Learning (SEL) implementation, extending beyond simply utilizing a PDF curriculum․ They must model SEL skills – self-awareness, self-management, social awareness, relationship skills, and responsible decision-making – in their interactions with students and colleagues․
Effective teachers create safe and supportive classroom environments where students feel comfortable expressing emotions and practicing these skills․ Observing a teacher like Jamalia Sheets modeling emotions demonstrates this in action․ They require professional development to understand SEL principles and integrate them into daily lessons․
Furthermore, teachers need to be equipped to identify students who may need additional support and connect them with appropriate resources․ Their consistent application of SEL strategies is paramount to fostering a school-wide culture of emotional intelligence․

SEL and School-Wide Positive Behavior Interventions and Supports (SWPBIS)
SEL and School-Wide Positive Behavior Interventions and Supports (SWPBIS) are increasingly recognized as complementary frameworks for creating positive school climates․ Both approaches prioritize proactive strategies to support student well-being and academic success, moving beyond reactive disciplinary measures․
SWPBIS provides a structured system for establishing clear behavioral expectations and teaching those expectations to students․ Integrating SEL skills into this framework enhances its effectiveness by addressing the underlying emotional and social factors that contribute to behavior․
For example, Reynolds Middle School’s return to distance learning due to behavioral issues highlights the need for both systems․ SEL equips students with the skills to manage emotions and make responsible decisions, while SWPBIS provides the consistent structure and support needed to reinforce those skills․
Current Controversies and Criticisms Surrounding SEL
Despite growing adoption, Social Emotional Learning (SEL) faces increasing scrutiny and controversy, mirroring past debates surrounding educational initiatives like Common Core and Critical Race Theory․ Concerns often center on the perceived ideological underpinnings of SEL curricula and potential overreach into areas traditionally considered parental responsibility․
Critics question whether SEL programs promote specific political or social agendas, fearing indoctrination rather than genuine skill development․ The lack of standardized curricula and varying implementation approaches contribute to these anxieties, as content can differ significantly across districts․
Furthermore, some argue that focusing on emotional well-being detracts from academic rigor․ These debates highlight the need for transparency, community engagement, and careful consideration of curriculum content to address legitimate concerns and ensure SEL benefits all students․
Future Trends in Social Emotional Learning
Looking ahead, SEL is poised for continued evolution, driven by technological advancements and a deeper understanding of the brain․ Expect increased integration of SEL into digital learning platforms, offering personalized and adaptive emotional support for students․

Furthermore, a growing emphasis on culturally responsive SEL curricula will address the diverse needs of student populations, ensuring inclusivity and relevance․ Research will likely focus on refining SEL measurement tools and demonstrating long-term impacts on academic achievement and life success․
The convergence of SEL with mental health initiatives is also anticipated, creating more comprehensive support systems for students․ Ultimately, the future of SEL hinges on collaborative efforts between educators, researchers, and policymakers to create effective and equitable programs․



